Mammals and insects are the two most abundant and diverse groups of animals on Earth,
Mammals and insects are the two most abundant and diverse groups of animals on Earth, although there are huge biological differences between these two groups, they both follow the evolutionary laws of the world. biological kingdom.
One of the most striking differences is that males and females have sexually dimorphic body sizes. In most mammals, males are larger than females, while in insects the opposite is true. And this sexual dimorphism expressed differently in different species has aroused the interest and curiosity of biologists.
Why are males larger than females in most mammals?
One reason most mammal males are larger than females is that they need more food to get larger body sizes and defend territory and fight other males. Males are often more active than females, for example, male lions need to run faster to protect their pack from other male lions that are invading its territory.
In addition, males also need to expend more energy than they produce and maintain fertility. Therefore, they need more food to meet their body's nutritional needs.
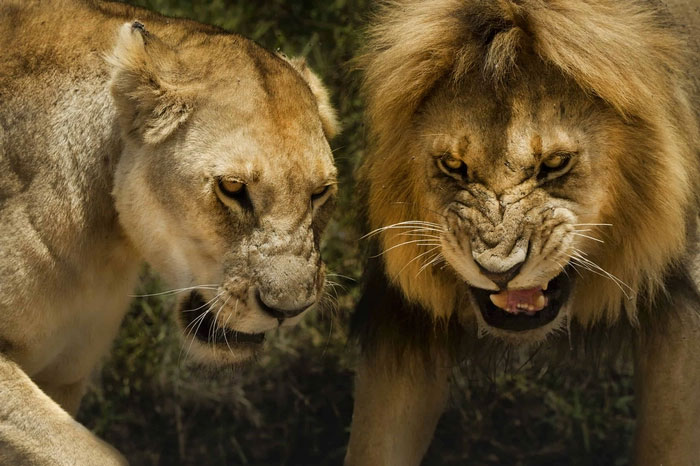

In mammals, intense competition often occurs between males.
Sexual dimorphism simply means that there are morphological differences between males and females in addition to differences in their sex organs. These characteristics can include body size, color, weight, body shape, some appendages, and even behavioral differences.
In mammals, intense competition often occurs between males. For example, male gorillas will compete for resources and females in the territory, male seals will compete for females in the breeding area...
In this competition, larger males will be more powerful and often more aggressive, and can compete more effectively for resources, females. As a result, larger males will have a more competitive advantage, and this advantage is gradually preserved, leading to a difference in body size between males and females.
In addition, biologists suggest that male mammals are more susceptible to physical mutations than females, which also results in larger males than females. This opportunity may arise through a gene mutation or other genetic variation.
If this change in size helps males compete more effectively for resources and mates, then the mutant gene will be preserved and passed on to the next generation.
In many mammals, females also show a preference for larger males. This selection increases the probability of successful survival of the next generation. This preference may therefore also promote the prevalence of large males in the population.
This is why the males of most mammals are larger than the females. Of course, in some particular species, this difference in size may not be obvious.
Mammals and insects are the two most abundant and diverse groups of animals on Earth, although there are huge biological differences between these two groups, they both follow the evolutionary laws of the world. biological kingdom.
One of the most striking differences is that males and females have sexually dimorphic body sizes. In most mammals, males are larger than females, while in insects the opposite is true. And this sexual dimorphism expressed differently in different species has aroused the interest and curiosity of biologists.
Why are males larger than females in most mammals?
One reason most mammal males are larger than females is that they need more food to get larger body sizes and defend territory and fight other males. Males are often more active than females, for example, male lions need to run faster to protect their pack from other male lions that are invading its territory.
In addition, males also need to expend more energy than they produce and maintain fertility. Therefore, they need more food to meet their body's nutritional needs.
In mammals, intense competition often occurs between males.
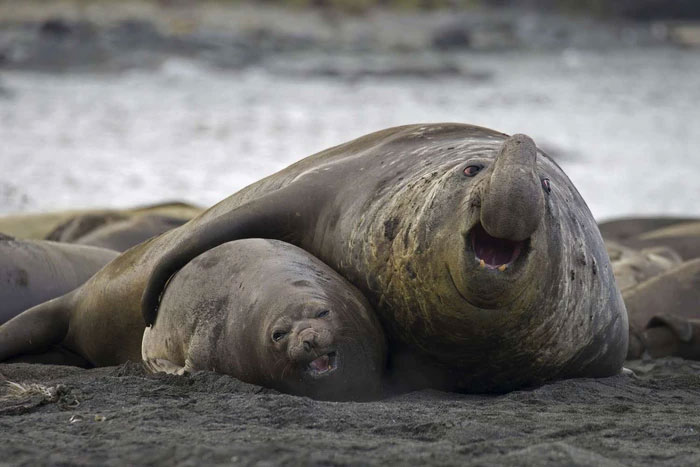

Females also show a preference for larger males.
Why are male insects smaller than females?
In most insects, females are larger than males. During insect reproduction, males only need to provide genetic information, while females need to expend a lot of energy to produce offspring, including finding nests, gathering food, incubating eggs, etc. .
Therefore, male insects do not need to increase in size to support behavioral needs like mammal males. Instead, they can reduce in size and spend energy developing reproductive resources.
In addition, insects often find mates and food by flight, and the small size of males is useful for moving freely between branches and grass.
Wolf Blanckenhorn, of the Zoological Museum at the University of Zurich, told LiveScience: "While females in insects are growing in size, males are devoting their energy and resources to growth. reproductive organ is much larger and more complex than in females - and compared to overall body size, it is also significantly larger than in mammals."
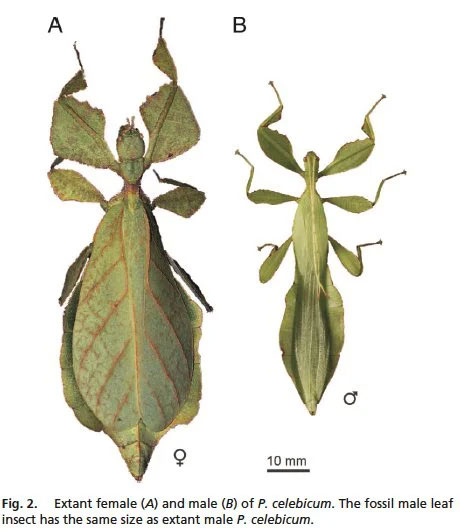
For most insects, body size varies widely between males and females. In general, females are much larger than males. This is especially obvious when you see a male and female side by side.
In general, males are larger than females in most mammals and vice versa in insects. This sexual dimorphism differs in different species due to biological evolution and adaptive evolution.
Male mammals need to increase in body size to support physiological and behavioral needs, as well as gain competitive and reproductive advantages; while the insects' lifestyle and feeding habits dictate that they can reduce their body size and invest energy and resources in superior reproduction.
These biological differences make the size differences of mammals and insects so important, provide rich research literature and evolutionary cases, and provide perspectives and new ideas for biological research and biodiversity conservation.